Tile patterns and grout tips that reduce maintenance
Choosing the right tile layout and grout can make daily upkeep simpler and prevent common issues like staining, mold, and cracked tiles. This article outlines practical tile patterns, grout selections, and installation considerations that reduce long-term maintenance while supporting remodel goals for showers, vanities, and overall waterproofing.
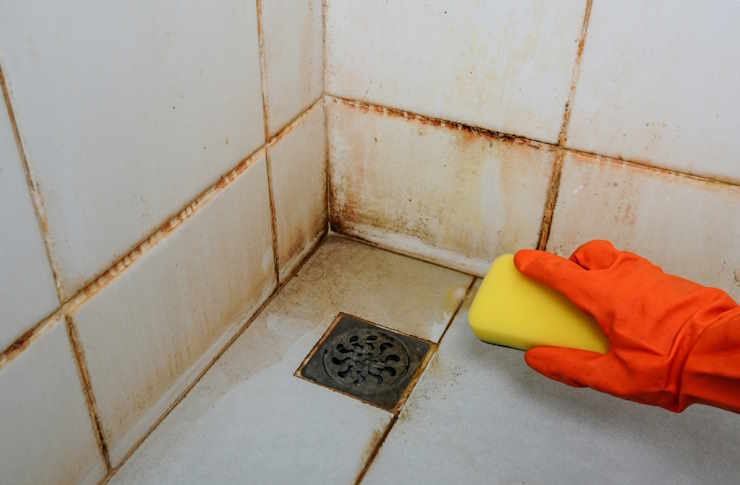

How do tile patterns affect maintenance?
Tile pattern choices influence how dirt, water, and grout lines behave. Larger-format tiles mean fewer grout joints, which generally lowers the area where grime and mold accumulate. Patterns such as straight-set or stacked layouts create uniform grout lines that are easier to clean than intricate mosaics or herringbone where grout crevices can trap soap scum. In wet areas like a shower, consider tile sizes and slip resistance: fewer joints and slightly textured tile surfaces balance cleanability with safety. When planning a remodel, coordinate tile selection with drainage slopes and fixture placement to prevent water pooling around sensitive seams.
Which grout choices lower long-term upkeep?
Selecting the right grout is central to maintenance. Epoxy grout resists stains and moisture better than traditional cementitious grout, making it a good option for showers and floors near drains. Cementitious grouts with polymer additives offer improved durability and are easier to work with for DIY projects. Sanded grout is stronger for wider joints, while unsanded suits narrow joints without scratching polished tiles. Sealing cement-based grout periodically helps reduce staining and mold growth; sealed grout still needs regular cleaning but tolerates exposure better. Match grout color thoughtfully—medium tones can hide minor discoloration versus stark white, reducing the visible need for frequent deep cleaning.
How to design remodels for shower, drainage, and fixtures?
A practical remodel considers tile layout in relation to shower drains, plumbing, and fixtures. Plan tile pattern and joint direction to align with slopes toward the drain; diagonal patterns can complicate slope calculation and increase cutting at fixtures. Use waterproofing membranes beneath tiles to protect subfloors and plumbing penetrations. Position fixtures so grout lines do not end awkwardly against a surround or drain, which can create weak spots. For curbless showers, choose thermal and slip-resistant tiles that maintain a consistent slope without excessive grout transitions. Proper underlayment and professional tile setting reduce future maintenance caused by loose or cracked tiles.
How can vanity, storage, and accessibility choices help upkeep?
Vanity design and storage affect cleaning ease and overall maintenance. Floating vanities lift cleaning above the floor line, making it easier to mop and reducing moisture accumulation at base junctions that can degrade grout and lower waterproofing effectiveness. Built-in storage niches in showers should be tiled with continuous drainage planning to avoid water traps; shelves with slight slopes and adequate waterproofing limit standing water. For accessibility, reducing thresholds and choosing continuous tile surfaces simplifies both cleaning and mobility. Selecting fixtures and hardware that minimize seams where water can collect—such as wall-mounted faucets—also helps preserve grout and tile integrity.
What role do lighting, ventilation, and plumbing play in tile longevity?
Good lighting and ventilation complement tile and grout selection by preventing moisture-related deterioration. Proper ventilation reduces humidity, cutting the risk of mold in grout lines and behind tiles; a vent fan rated for the room size and positioned effectively is a cost-effective maintenance strategy. Adequate lighting reveals soiling early and makes maintenance tasks easier. Plumbing choices that limit leaks—quality fixtures and accessible shutoffs—prevent prolonged water exposure that can undermine grout and waterproofing. Regular inspection of grout around drains and fixtures helps catch seal failures early, reducing the scope of repairs.
How to choose tiles for sustainability and improved waterproofing?
Sustainable tile options include porcelain and certain ceramic tiles made with recycled content or lower-energy manufacturing processes. Porcelain offers low porosity and strong resistance to moisture, contributing to waterproofing performance when combined with correct underlayment and thin-set. Consider tile finishes that balance cleanability and slip resistance: matte or textured finishes can be easier to maintain in wet zones than highly polished surfaces that show water spots. Incorporate waterproof membranes, proper drainage, and grout compatible with water exposure to ensure longevity. Selecting durable materials upfront supports sustainability by reducing the need for replacement and repairs.
Conclusion Tile patterns and grout choices are practical levers to reduce bathroom maintenance. Thoughtful planning—larger-format tiles where appropriate, grout type and color selection, reliable waterproofing, and attention to ventilation and plumbing—lowers cleaning frequency and extends the life of showers, vanities, and fixtures. A coordinated approach during remodels supports accessibility and storage goals while keeping long-term upkeep manageable.