Recognizing Behavioral Triggers and How to Address Them Safely
Understanding what prompts changes in a pet’s behavior enables owners to respond calmly and keep animals safe. This short overview previews common triggers, practical prevention strategies, and safe responses to reduce stress for both pets and caregivers.

Recognizing behavioral triggers in pets is a key skill for responsible ownership. When an animal reacts aggressively, fearfully, or unusually withdrawn, that response often stems from an identifiable trigger—pain, hunger, unfamiliar people, or changes in routine. Observing context, body language, and environmental cues helps you identify patterns so you can adapt care and reduce risk. Building predictable routines and gentle responses improves pet welfare and lowers the chance of escalation while supporting long-term behavior change.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
How does health and nutrition affect behavior?
Physical health and diet strongly influence temperament and reactions. Nutritional imbalances, dehydration, or sudden changes in diet can increase irritability or lethargy. Underlying medical issues such as dental pain, gastrointestinal upset, or endocrine disorders also show up as behavior changes. Regular veterinary checkups, consistent feeding schedules, and monitoring hydration support stable behavior. When you notice a sudden shift—pacing, snapping, or hiding—first consider health and nutrition as possible causes before assuming a training problem.
How do senior care and mobility issues change behavior?
Aging pets often develop mobility limits, sensory decline, and chronic pain that can alter behavior. Reduced hearing or vision can make animals more easily startled, while arthritis or joint pain may cause guarding, growling, or avoidance of handling. Adjusting living spaces for accessibility, providing senior-appropriate nutrition and supplements, and managing pain under veterinary guidance can reduce stress-related reactions. Observing when behaviors occur—after exertion, in the morning, or during handling—helps pinpoint mobility- and age-related triggers.
Can training and grooming reduce behavioral triggers?
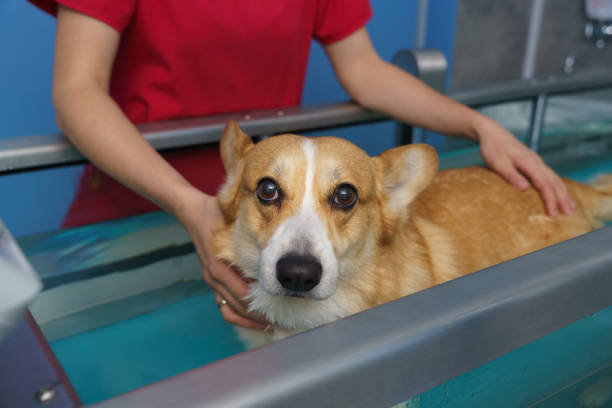
Consistent, positive training builds predictable responses and reduces fear-driven reactions. Training that emphasizes rewards, gradual desensitization, and counter-conditioning teaches pets to associate previously stressful stimuli with neutral or pleasant outcomes. Grooming routines introduced slowly and paired with treats or calm praise make handling less triggering. Professional trainers and groomers who use fear-free techniques can guide gradual exposure and safe handling strategies for animals with strong reactions.
How do exercise, socialization, and enrichment help?
Regular exercise and mental enrichment reduce stress and excess energy that can amplify reactive behavior. Structured play, puzzle feeders, and rotating toys provide stimulation while helping pets cope with boredom or anxiety. Controlled socialization—short, supervised positive interactions with other animals and people—builds confidence and reduces fear of novel situations. Tailoring exercise intensity and enrichment to age, mobility, and health ensures benefits without causing physical strain that could lead to defensive reactions.
What safety and emergency steps protect pets?
Create safe routines and plan for emergencies to reduce trigger exposure and respond effectively when incidents occur. Use barriers, leashes, or muzzles where required for temporary safety, and ensure everyone in the household understands handling protocols. Keep a basic pet first-aid kit, and know the contact details for local veterinary emergency services or clinics in your area. In an acute behavioral crisis, prioritize human and animal safety: remove bystanders, avoid sudden movements, and seek professional help rather than attempting risky restraint.
How to manage allergies, travel, and hydration?
Allergies, travel stress, and dehydration can each act as behavioral triggers. Allergic reactions may cause itchiness or discomfort that increases agitation; addressing environmental allergens and using vet-recommended treatments helps. Travel and unfamiliar environments can provoke anxiety—acclimate pets gradually to carriers and short trips, and maintain routines for feeding and water. Ensuring regular access to fresh water, monitoring for signs of heat stress, and minimizing sudden environmental changes reduce the chance that these factors will trigger adverse behaviors.
Conclusion Identifying and addressing behavioral triggers requires attention to health, routine, and environment. By considering nutrition, medical status, age-related mobility, training methods, exercise and enrichment, and practical safety measures, owners can reduce triggers and respond more safely. Collaborative work with veterinarians, trainers, and groomers helps create tailored plans that protect both pets and people while promoting long-term well-being.