Daily movement routines to improve strength and posture
Short daily movement routines can steadily improve strength and posture when combined with mobility work, proper nutrition, and recovery. This article outlines practical, sustainable steps you can weave into everyday life to build resilience, tone muscles, and support overall wellness.
Daily movement matters for both physical function and how you feel throughout the day. Establishing a short, consistent routine that includes mobility work, strength-focused exercises, posture checks, and breathwork encourages more stable alignment, better endurance for daily tasks, and improved muscle tone over time. Consistency and gradual progression are key: start with manageable sets and simple movements, then increase intensity or volume as your body adapts. Include basic nutrition and hydration habits to support recovery and skin health alongside the exercise routine.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
Movement: building a daily habit
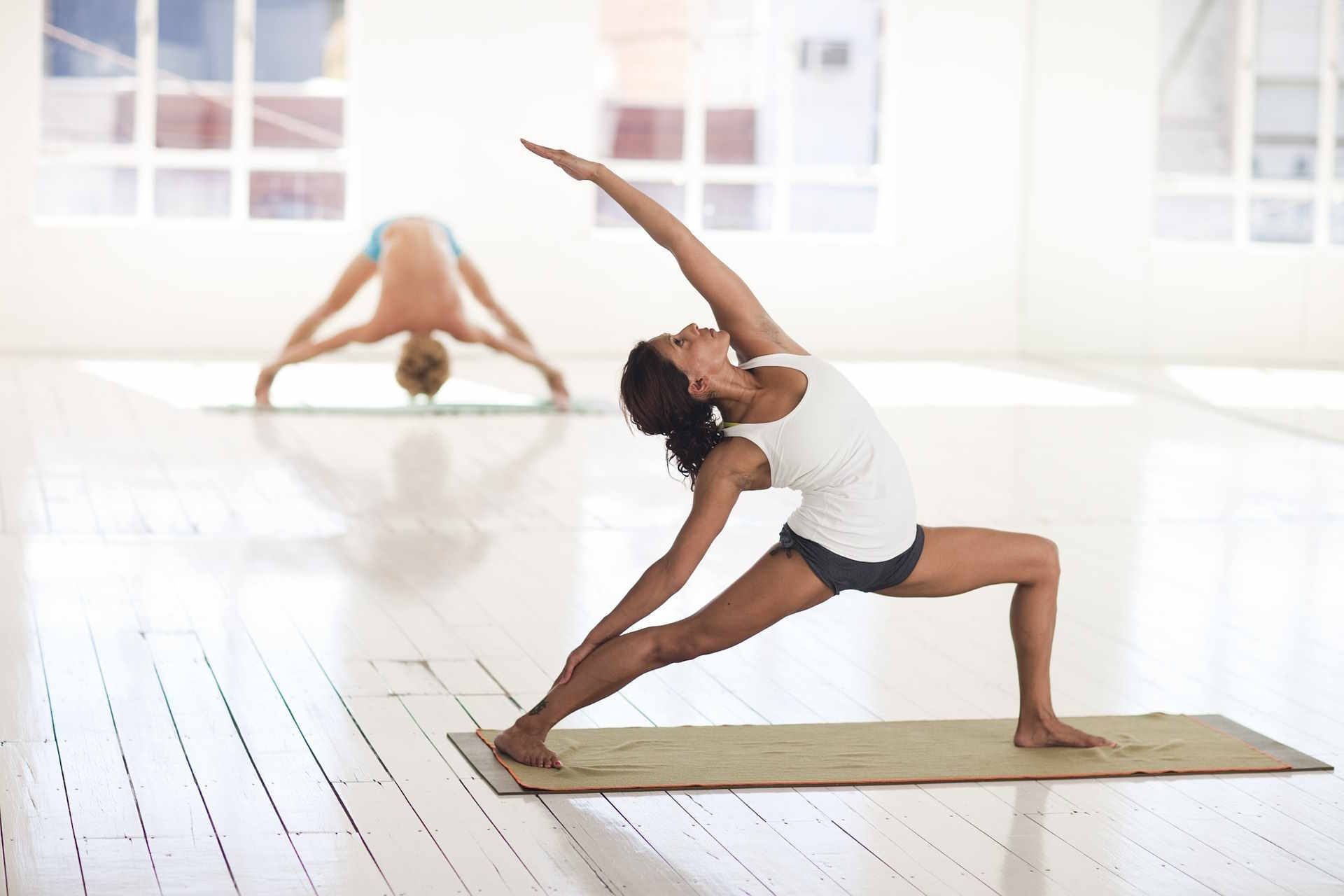
Daily movement is about frequency rather than duration. Aim for short sessions spread across the day: a 10–20 minute morning routine, short movement breaks during work, and a light evening mobility sequence. Simple practices—walking, bodyweight squats, or a few sets of push-ups—help maintain blood flow, reduce stiffness, and establish a habit of regular activity. Track small wins (consistency, added reps, improved posture during tasks) to reinforce the routine and make movement a reliable part of daily life.
Mobility: gentle joint work
Mobility exercises focus on improving range of motion around key joints—shoulders, hips, spine, and ankles. Include dynamic movements like leg swings, thoracic rotations, and controlled hip circles to maintain lubricated joints and reduce mechanical stress. Perform mobility work before strength sessions or after prolonged sitting to prepare tissues for load and reduce compensatory patterns. Gentle mobility also supports flexibility and makes strength work safer and more effective over time.
Strength: brief resistance sessions
Strength improvements do not require long gym sessions. Two to four short resistance sessions per week using bodyweight, resistance bands, or light weights can increase muscle tone and functional capacity. Prioritize compound patterns—hinge, squat, push, pull, and carry variations—to build balanced strength. Focus on controlled tempo and full range of motion, and allow at least 48 hours of recovery for the same muscle groups. Gradual progression—adding reps, sets, or resistance—supports resilience and helps prevent injury.
Posture: alignment strategies
Improving posture involves both strengthening weak muscles and reducing habitual poor positions. Integrate posture checks into your routine: set neutral spine reminders, perform scapular squeezes, and strengthen the posterior chain (glutes, hamstrings, back extensors). Ergonomic adjustments to your workspace and mindful breathing can reduce forward head carriage and collapsed shoulders. Small, regular corrections are more effective than occasional intense efforts; over time these adjustments become automatic and improve how you carry yourself daily.
Flexibility and breathwork
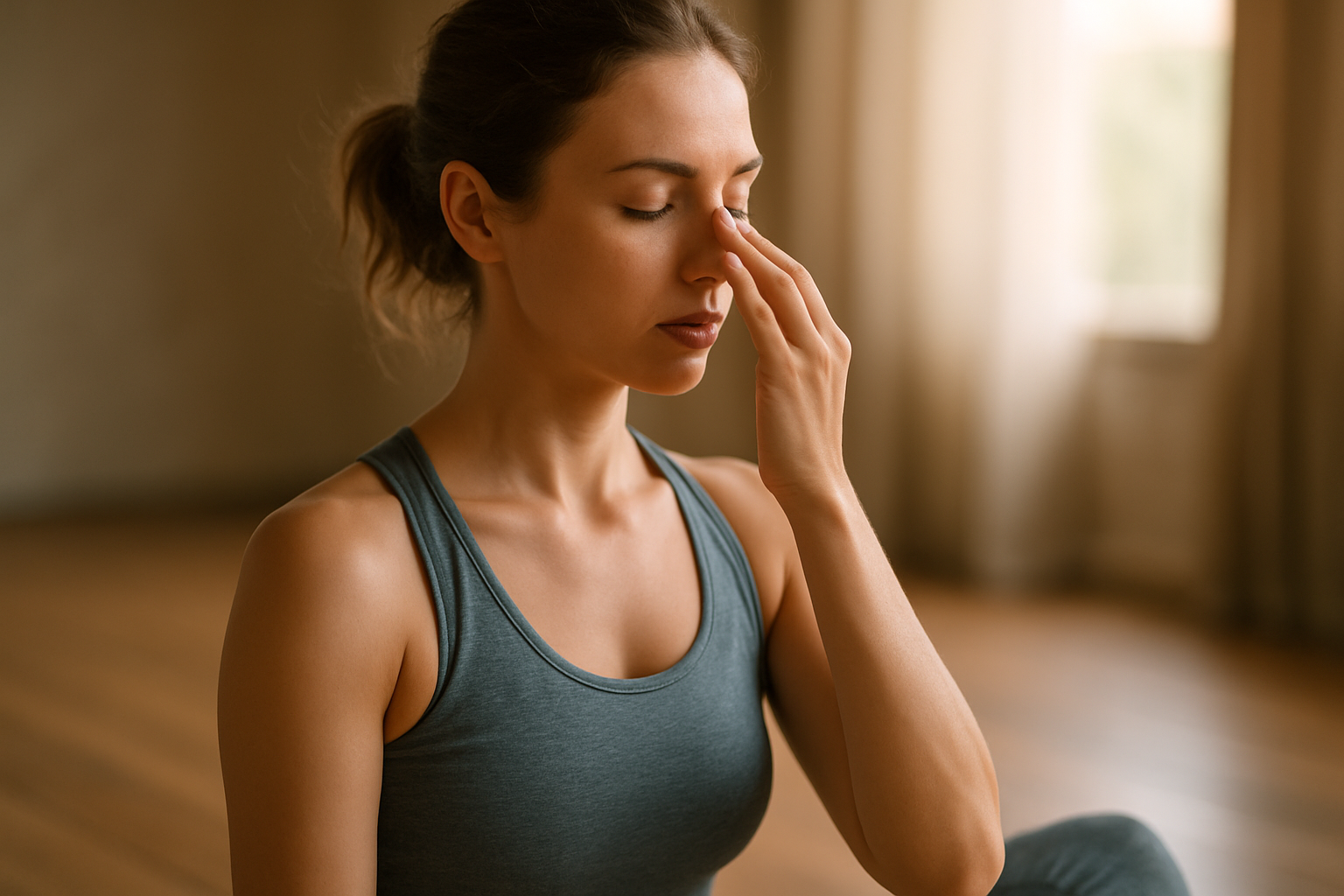
Flexibility work complements strength and mobility by addressing tight tissues that limit movement. Incorporate static stretches for areas that feel restricted—hip flexors, chest, and calves—after workouts or during evening routines. Pair stretching with simple breathwork: diaphragmatic breathing helps regulate nervous system tone, improve core stabilization, and enhance relaxation during recovery. Consistent breath practice also supports endurance and can reduce tension that negatively affects posture and movement quality.
Recovery, nutrition, skincare and hydration
Recovery is essential for gains in strength, posture, and overall wellness. Prioritize sleep, adequate protein intake, and consistent hydration to support tissue repair and endurance. Balanced nutrition—lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats—provides the building blocks for muscle tone and resilience. Hydration supports joint function and skin health; paired with gentle facial massage and sun protection, movement that increases circulation can complement skincare routines. Plan active recovery days with light movement and focused mobility work to maintain progress without overtaxing the body.
Regular routines are sustainable when they fit into daily life. Start with realistic time commitments, combine mobility with strength and breathwork, and adjust intensity slowly to build resilience. Track improvements in posture, easier performance of daily tasks, and increased endurance rather than short-term aesthetic outcomes. With consistent application, these movement habits contribute to long-term strength, better alignment, and overall wellness.
Conclusion A balanced daily movement routine that weaves together mobility, strength, posture work, breathwork, and sensible recovery habits supports gradual improvements in muscle tone and alignment. Emphasize consistency, gradual progression, and supportive nutrition and hydration to help your body adapt safely and sustainably over time.