Adapting routines for seasonal skin changes and sensitivities
Seasonal shifts can alter skin behavior, from drier winters to oilier summers, and people with sensitivities may notice flare-ups when humidity, temperature, or pollution change. Adjusting routines intentionally helps maintain barrier health while keeping products effective across conditions.
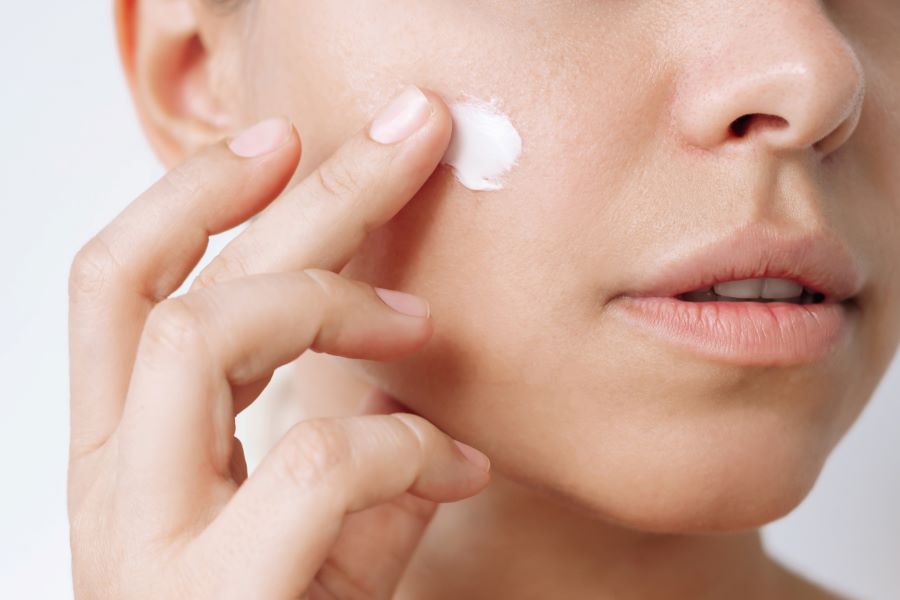

Seasonal changes often mean different challenges for the skin: reduced humidity and indoor heating can dry the skin in winter, while heat and sweat in summer can increase oiliness and sensitivity. Adapting routines—rather than switching everything at once—lets you respond to fluctuating needs while minimizing irritation. This article outlines practical changes to your daily regimen, highlights thoughtful ingredient choices and formulation considerations, and explains how to monitor reactions so you can protect skin health year-round.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
How does skincare respond to seasonal shifts?
Skin’s barrier function, sebum production, and water retention change with temperature and humidity. In cold months, reduced humidity and indoor heating accelerate transepidermal water loss, increasing dryness and sensitivity. In warm seasons, sweat and oil can trap dirt and trigger congestion or acne. Observing how your skin feels—tight, flaky, red, or congested—helps tailor steps like layering products, timing exfoliation, and altering sunscreen use. Gentle cleansing and maintaining barrier-supporting steps are foundational in any season to prevent overreaction when conditions change.
How should cosmetics, ingredients, and formulation be chosen?
When selecting cosmetics, look beyond claims to the ingredient list and formulation type. Lighter emulsions and water-based formulations suit humid months, while oil-based balms or richer creams help in dry climates. Ingredients like humectants (hyaluronic acid), occlusives (squalane, ceramides), and emollients provide different benefits: humectants draw water, occlusives lock it in, and emollients smooth the surface. Avoid products with unnecessary fragrance or high concentrations of irritants during transition periods. Patchtest new formulations on a small skin area to check tolerance before full-face use.
When should dermatology and patchtest be part of your plan?
If seasonal changes trigger persistent redness, itching, severe flaking, rashes, or acne that over-the-counter adjustments don’t resolve, consult a dermatologist. A professional can distinguish eczema, rosacea, contact dermatitis, or other conditions and recommend appropriate prescription or in-office treatments. For everyday choices, perform a patchtest for new serums, cosmetics, or actives: apply a small amount behind the ear or on the inner forearm for 48–72 hours to observe reactions. This reduces risk of full-face reactions to preservatives, fragrances, or high-potency actives.
How to adjust serums and moisturizer routines with actives like hyaluronic and niacinamide?
Serums deliver concentrated actives—hyaluronic for hydration, niacinamide for barrier support and tone, peptides for firmness, and antioxidants for environmental protection. In winter, prioritize hyaluronic serums followed by a richer moisturizer to trap hydration; layering a humectant with an occlusive is effective. In summer, switch to lighter serums and gel moisturizers that contain niacinamide to regulate sebum and support the barrier. Use peptides consistently if tolerance is good, as they’re generally well tolerated. Introduce one active at a time and allow the skin to adjust before combining strong actives to reduce irritation risk.
What role do exfoliation and preservatives play across seasons?
Exfoliation frequency often needs adjusting: gentle, chemical exfoliants like low-concentration AHAs or PHAs can help with winter flakiness when used sparingly, whereas in summer, careful use prevents over-exfoliation and sun sensitivity. Physical scrubs may aggravate sensitive skin and are usually best avoided during flare-ups. Preservatives are essential in multi-ingredient cosmetics to prevent microbial growth; however, some preservatives can irritate sensitive skin. Opt for formulations with well-tolerated preservative systems and always perform a patchtest when switching brands or product types to ensure compatibility.
How to prioritize sunscreen, antioxidants, and peptides year-round?
Sunscreen remains a constant necessity: UV exposure and photodamage occur in all seasons. Choose broad-spectrum sunscreen appropriate for your skin type—lighter lotions or gel formulas for oily/hot months, cream-based sunscreens for dry periods. Antioxidants such as vitamin C or mixed antioxidant blends can be used beneath sunscreen to neutralize environmental stressors, but introduce them gradually to monitor tolerance. Peptides and barrier-repair ingredients can be used continuously to support resilience. Remember that some actives increase photosensitivity; if using AHAs or retinoids seasonally, be diligent with daily sunscreen.
Seasonal sensitivity management is about observation, gradual changes, and consistent core steps. Keep cleansing gentle, tailor moisturizer texture to the climate, introduce or reduce exfoliation depending on barrier health, and use targeted serums for hydration and barrier support. Patchtest new formulations, consult dermatology for persistent issues, and prioritize sunscreen and antioxidants year-round to reduce environmental damage.
Adapting routines for seasonal skin changes and sensitivities relies on informed choices rather than frequent overhauls. Focus on barrier protection, suitable formulations, and measured use of actives to maintain skin balance through changing weather and conditions.